
Job Opportunity Investment Network (JOIN) Workforce Learning Community: 2018-2021 Data Report
These summary findings provide a snapshot in time (November 2020) of the outcomes for the JOIN CBOs that participated in the Fall 2019/Winter 2020 WBN survey. Data submitted to the national WBN survey were analyzed from 14 JOIN programs operated by 14 organizations and 77 National programs from 51 organizations.
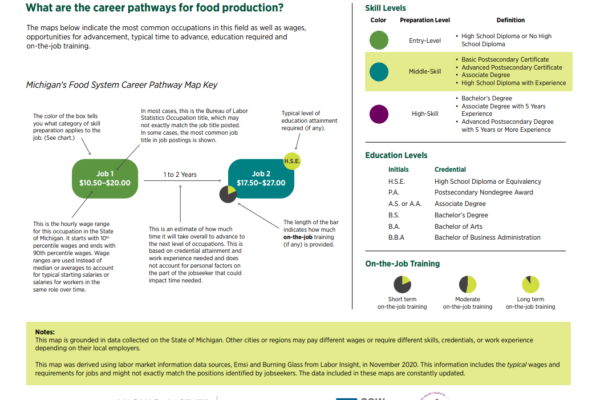
Food Production Career Pathway Maps – Michigan Local and Regional Food System Workforce Assessment
The food production pathway encompasses occupations involved in the growing and raising of Michigan foods. It encompasses crop production and animal production, as well as fishing, hunting, and trapping. Most jobs in Michigan within this subsector are in crop production.
What the Detroit Economic Mobility Grants Can Teach Us
The Detroit Economic Mobility Grant initiative demonstrated that adult education and occupational training programs can work together to substantially improve learner results by accelerating instruction and contextualizing it to work. Ten organizations or pairs of workforce and adult education organizations received a total of nearly $1 million from 2018-2020 to pilot four evidence-based models for more effectively helping adults gain foundational skills crucial to employment opportunities.

Detroit Adult Foundational Skill Development: Challenges and Solutions
This report examines the state of foundational skills in Detroit as well as four evidence-based approaches being employed elsewhere in the country that produce improved results.
Applying Demand and Supply Signals
In April 2017, Connecting Credentials convened five workgroups of diverse leaders in credentialing reform to tackle particularly challenging aspects of achieving the vision of a learner-centered credentialing ecosystem articulated in the 2016 From National Dialogue to Collective Action: Building Learning-Based Credentialing Systems.

Learning to Thrive: How Data Can Fuel Better Workforce Development Results
This report describes the multi-year Twin Cities Benchmarking Initiative: its design and approach to capacity building, the role of funders in nurturing culture change, and the results achieved. It highlights the examples, lessons—and promise—that findings hold for workforce development nonprofits and their funders in other locales across the nation.
Preliminary Asset Map for SE MI AESS Cluster
AESSI Battery Show Booth Brochure
Detroit’s Untapped Talent: Partnerships and Pathways for Success
This report, the second of a two part series, is the culmination of a research effort to create a workforce system “map” which would inform a comprehensive and data-driven understanding of Detroit’s workforce development assets, opportunities, and challenges.

Apples to Apples: 2016 Data Update
This report provides information that will assist funders, policy makers and practitioners in understanding what “good” results are for different types of programs. Similar to the larger workforce field, the data represent a wide variety of populations served, strategies used and
organizational contexts.
Detroit’s Untapped Talent: Jobs and On-Ramps Needed
This report is the first of a two-part series detailing the findings from research conducted by CSW. It includes information about the complexities of Detroit’s resident labor pool, Detroit’s industry mix, and the mix of jobs and skills needed for the city to prosper.
Employing Opportunity Youth
Chronic disconnection affects a significant population of young people with far-reaching social and economic costs. These disconnected or “opportunity” youth are defined as 16-24 year olds who are not connected to school or work, and who have one or more barriers to entry into both. These young people are in very serious danger of being left behind permanently, often facing long-term unemployment, low or no income, and/or incarceration. The consequences of not helping these young people succeed are immediate, pressing, and will continue to reverberate both socially and economically until critical steps are taken to increase reconnection and sustainable employment.

